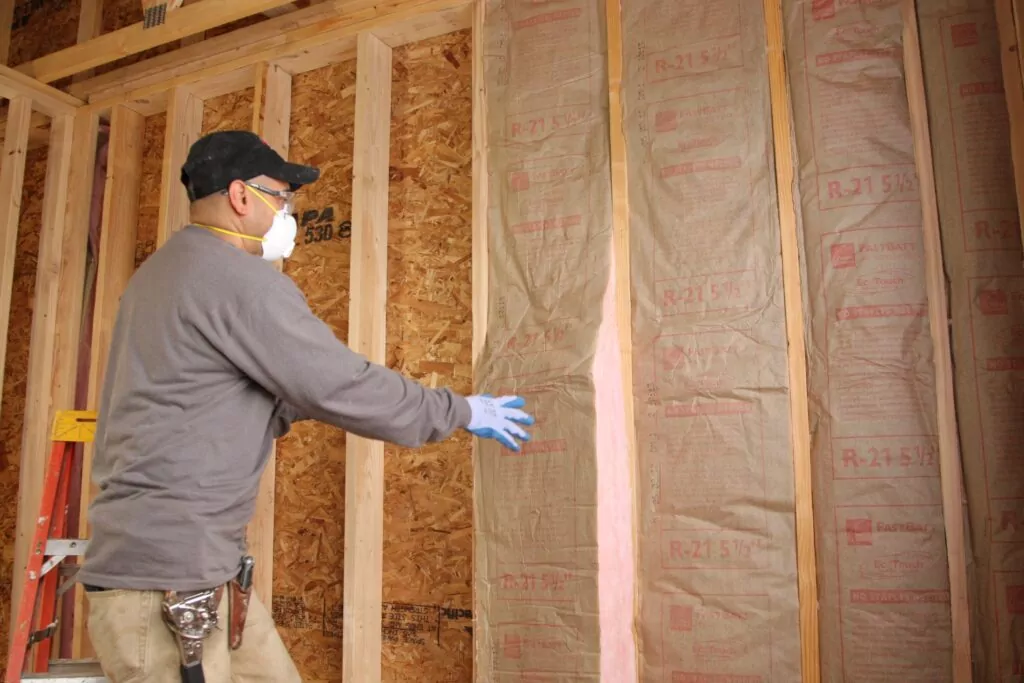
Insulation is the key to efficient heating and cooling. Like a thermos or a drink cooler, insulation keeps heated and cooled air inside where it belongs. Insulating efficiency is measured in thermal resistance, or R-value.
The R-value is a measurement of an insulation material’s heat resistance/ability to stop the transfer of heat (the R stands for “resistance”). This conveys a material’s ability to resist heat transfer per inch of thickness. Higher R-values signify greater insulating power.
Call Mooney & Moses at (513) 341-8918 to install insulation and start living more energy efficiently, or keep reading to learn more about R-value.
Why Is R-Value Important?
A properly insulated home should reduce heat flow, helping keep warm air inside during winter and outside during summer. Reducing the flow of heat in your home keeps your energy costs low, so good insulation is essential, regardless of a home’s age or size.
Knowing the insulation R-values throughout your home tells you whether you have enough insulation based on where you live. Inadequate insulation can lead to comfort problems and higher utility costs while achieving the recommended insulation levels makes your home more comfortable and energy-efficient.
How Is Insulation R-Value Calculated?
Here’s a quick example: Solid wood has an R-value of 1. An R-value is also calculated per inch of width. Therefore, a three-inch-thick board has an R-value of 3. Blown fiberglass installed in the attic has an R-value of 2.2 per inch, so 12 inches of it would give you an R-value of 26.4 in your attic installation project.
Choose the Right Insulation for Your Home
The type and amount of insulation you need depends on several factors, including the local climate and what area you’re insulating. Insulators with a high R-value tend to be more expensive and some homes in certain climates don’t need as much insulation as others.
For example, homeowners in northern Minnesota need insulation that can perform effectively in negative-digit temperatures, which is usually not much of a concern here in southwestern Ohio.
The Department of Energy came up with a system that rates different areas of the United States, recommending the ideal R-value for each region. The Cincinnati area is in zone 4.
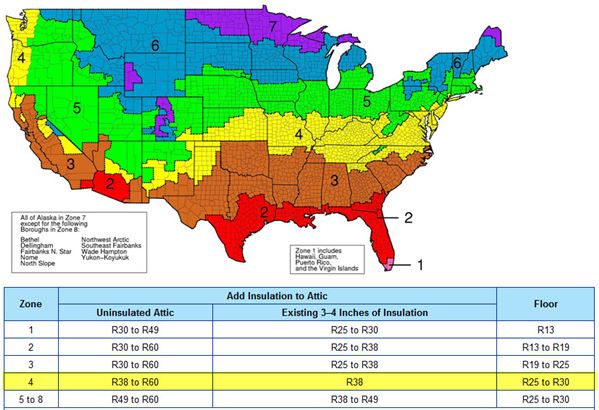
Referencing an insulation R-value chart can help you insulate your attic, walls, floors and crawl spaces adequately for your particular climate.
Which Insulation Has the Highest R-Value?
- Fiberglass insulation comes in batts, blankets, rolls and loose-fill, offering R-3.1 to R-4.3 per inch. Fiberglass is usually installed between wall studs, floor joists and ceiling rafters.
- Cellulose insulation is available in loose-fill form and is rated between R-3.2 and R-3.9. It’s appropriate for attics and wall cavities.
- Spray foam insulation comes in two forms — open-cell (R-3.5) and closed-cell (R-6.0 to R-6.5). Open-cell allows some air and moisture to travel through, while closed-cell provides an air and vapor barrier.
- Rigid foam board insulation is available in many materials, including polystyrene (R-3.8 to R-5.0), polyurethane (R-5.5 to R-6.5) and polyisocyanurate (R-5.6 to R-8.0). Since it has the highest R-value, rigid foam is typically reserved for foundations and basement walls.
If you’re ready to start your home insulation project, contact our team at (513) 341-8918 or online to get an estimate.
Contact Insulation Installers in Cincinnati, OH
Whether you know what insulation you want or you’re looking for personalized tips, the insulation experts at Mooney & Moses can help. We’ll make recommendations based on your needs and budget and install your preferred insulation quickly and affordably.
With over 65 years of experience, you know you’re in good hands with Mooney & Moses.
Insulation FAQs
How does insulation work?
To understand how insulation works, it helps to understand the three types of heat flow:
- Conduction: The flow of heat through a material.
- Convection: How heat circulates through liquids and gases.
- Radiation: The movement of heat in a straight line through anything solid in its path.
Regardless of the mechanism, heat flows toward cooler areas until the temperature equalizes. In the winter, heat flows from the conditioned living space to adjacent unheated areas, such as the attic, garage, crawl space and outdoors.
Insulation aims to slow the heat transfer that results in winter heat loss and summer heat gain. Most insulation materials, like cellulose and fiberglass, resist conductive and convective heat flow. Radiant barriers and reflective insulation reduce radiant heat flow.
What R-value do I need?
For the most cost-effective results, follow the recommended insulation R-values for your region:
- North/Northeast: Attic R-49–R-60 | 2×4 walls R-13–R-15 | 2×6 walls R-19–R-21 | floors & crawl spaces R-25–R-30
- West/Midwest: Attic R-38–R-60 | 2×4 walls R-13–R-15 | 2×6 walls R-19–R-21 | floors & crawl spaces R-25–R-30
- South/Southeast: Attic R-30–R-60 | 2×4 walls R-13–R-15 | 2×6 walls R-19–R-21 | floors R-25 | crawl spaces R-19–R-25
How do I know what insulation type I need?
Once you know the ideal R-value for different parts of your home based on where you live, choosing the right type of insulation comes down to the application and budget. Talk to an insulation contractor at Mooney & Moses to help you decide between cellulose, fiberglass, spray foam and rigid foam board.
Call 513-341-8918 today to request insulation services in the Cincinnati area.